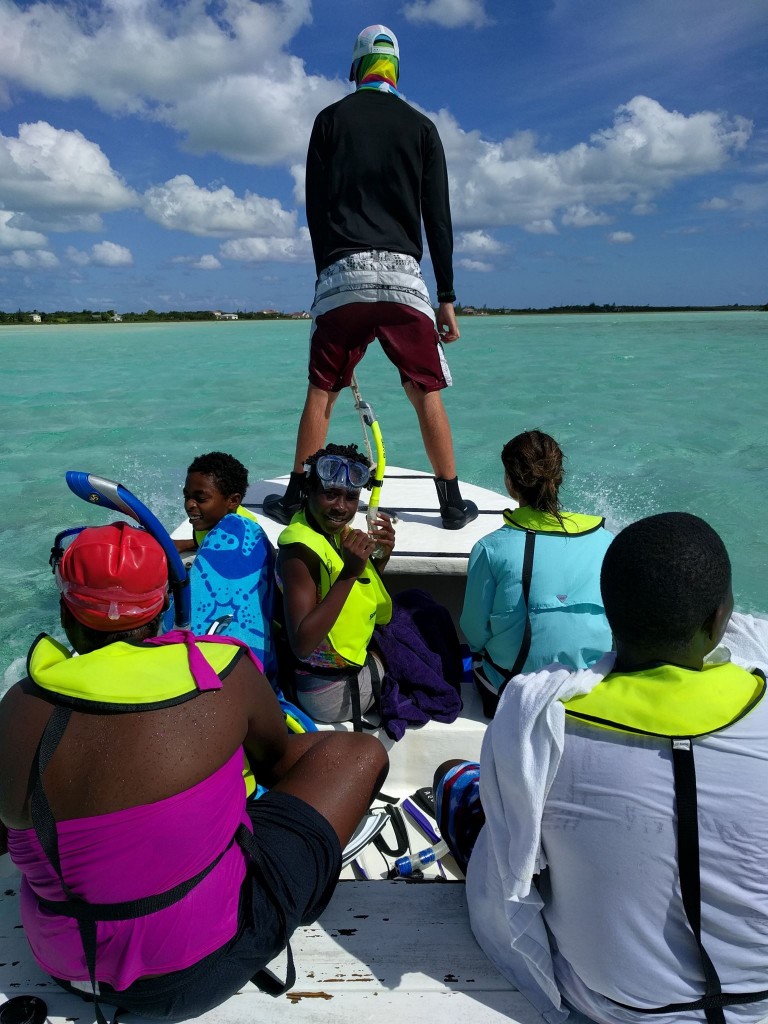
Last week, four members of staff from Cape Eleuthera Institute (CEI) visited Harbour Island as part of an outreach event working with the summer camp Space 2 Create.

Space 2 Create is a comprehensive summer enrichment program that hosts 83 students for 3 weeks. Through artistic, academic and community projects, youth are empowered as leaders. During morning session students focus on one of the following tracks;
- Space 2 Learn – math, English, science
- Space 2 Taste – culinary
- Space 2 Explore – marine science
- Space 2 Tell your story – film making
The CEI team spent two days teaching and interacting with the camp participants exploring different aspects of research and science.
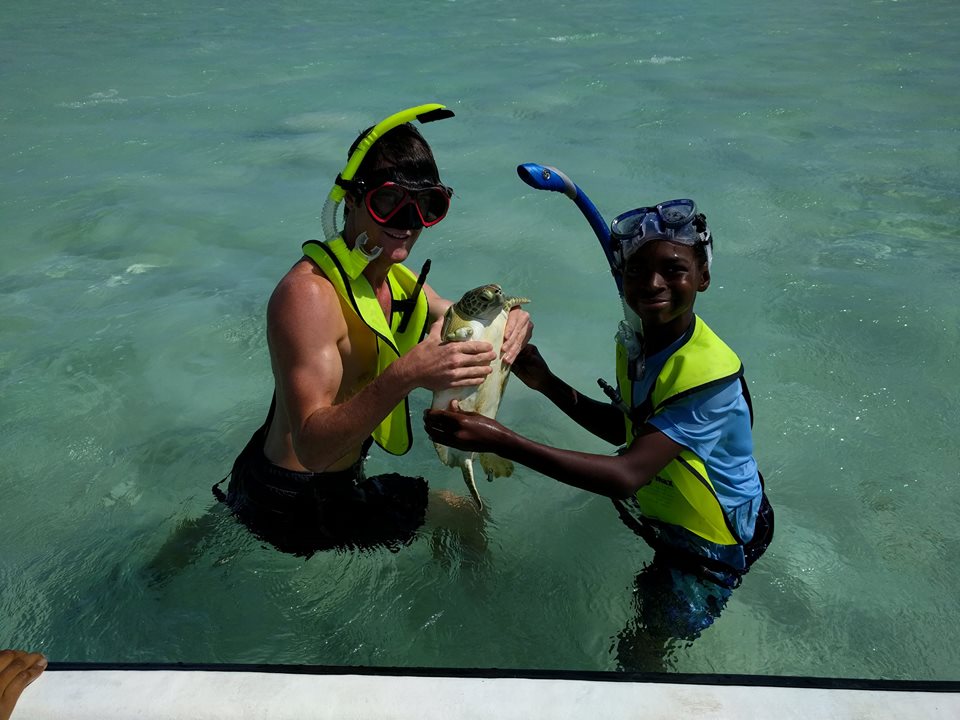
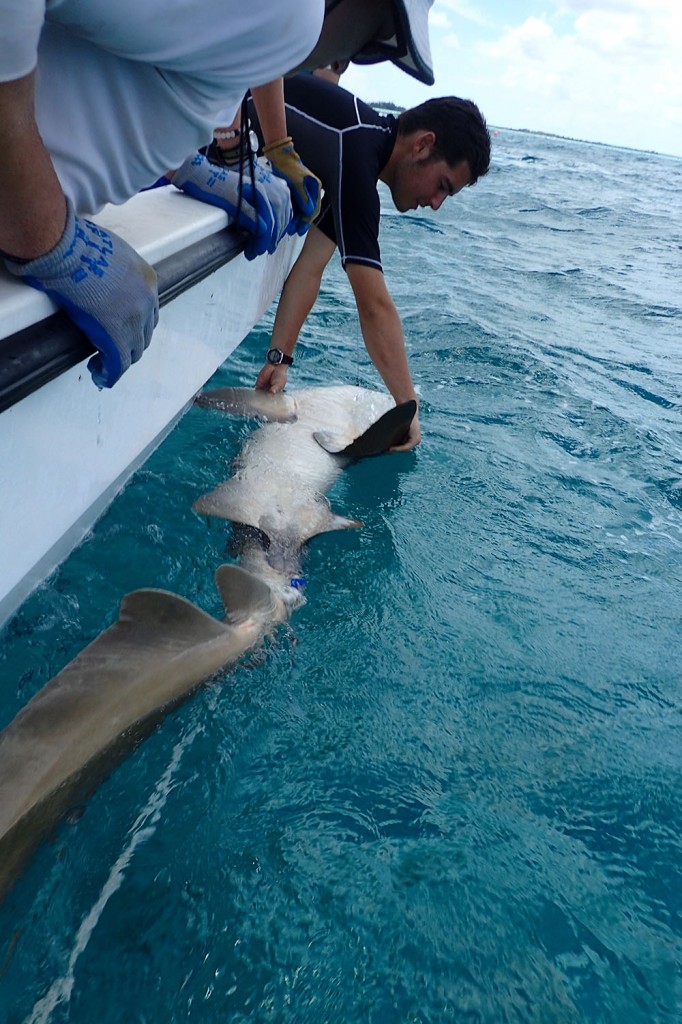
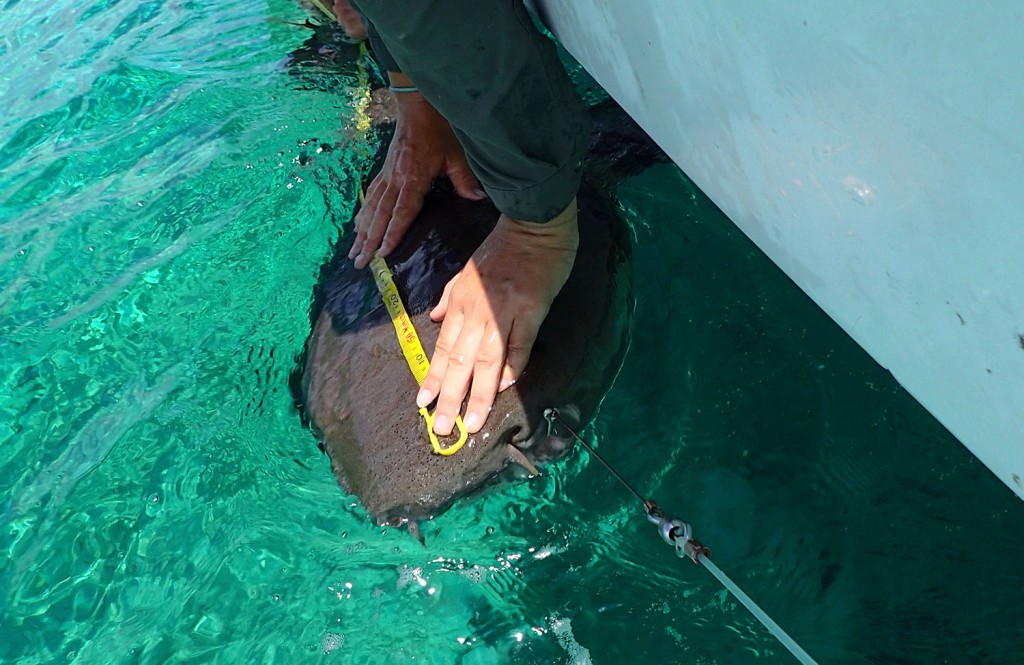
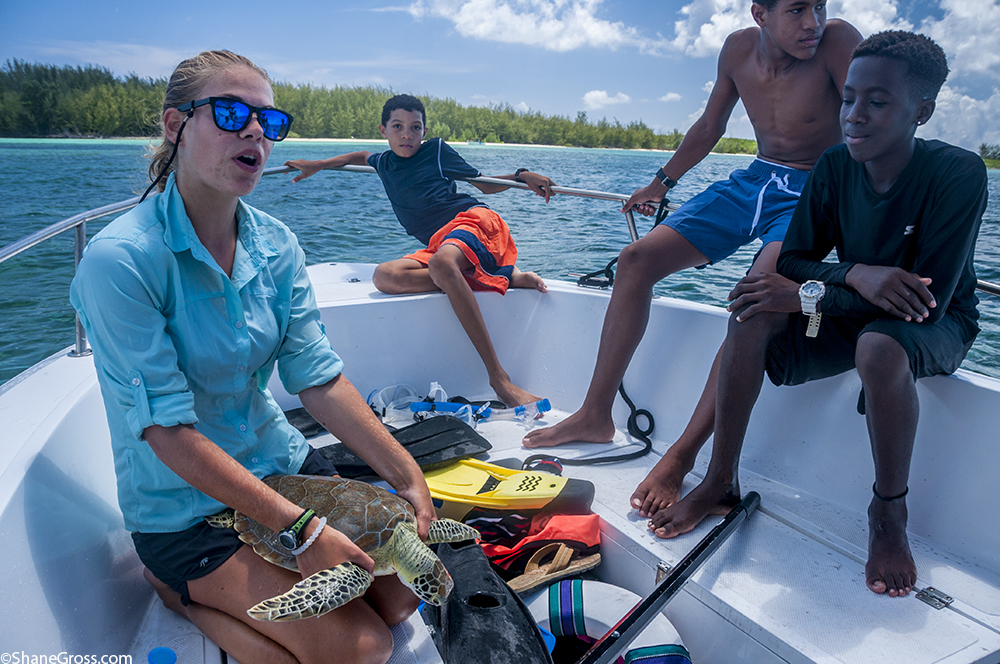
The first day Anna, Research Technician at CEI, gave a presentation about sea turtles in The Bahamas. The group learned about the four species of sea turtle in The Bahamas, and the threats they face. They also learned about their conservation status and the research being conducted currently at CEI. Following the presentation, the excited young students were able to go out in the field and participate in the capture of a green sea turtle contributing to the data they learned about earlier in the morning. They watched enthusiastically as measurements were taken and data was collected, and at the end of the workup were able to name and help safely release the animal. Green sea turtles are the most abundant of all 4 species found on Eleuthera, and are the main focus on the research conducted at CEI. Therefore the measurements taken from the turtle will allow researchers to gain important information such as growth rates and a health estimation of the individual, and contribute to a better understanding of the population of juveniles green sea turtles around Eleuthera.

The team was invited to stay for the remainder of the day to learn more about Space 2 Create and join in some of their afternoon activities. The afternoon was spent singing, dancing, painting, and joining in the drama class.
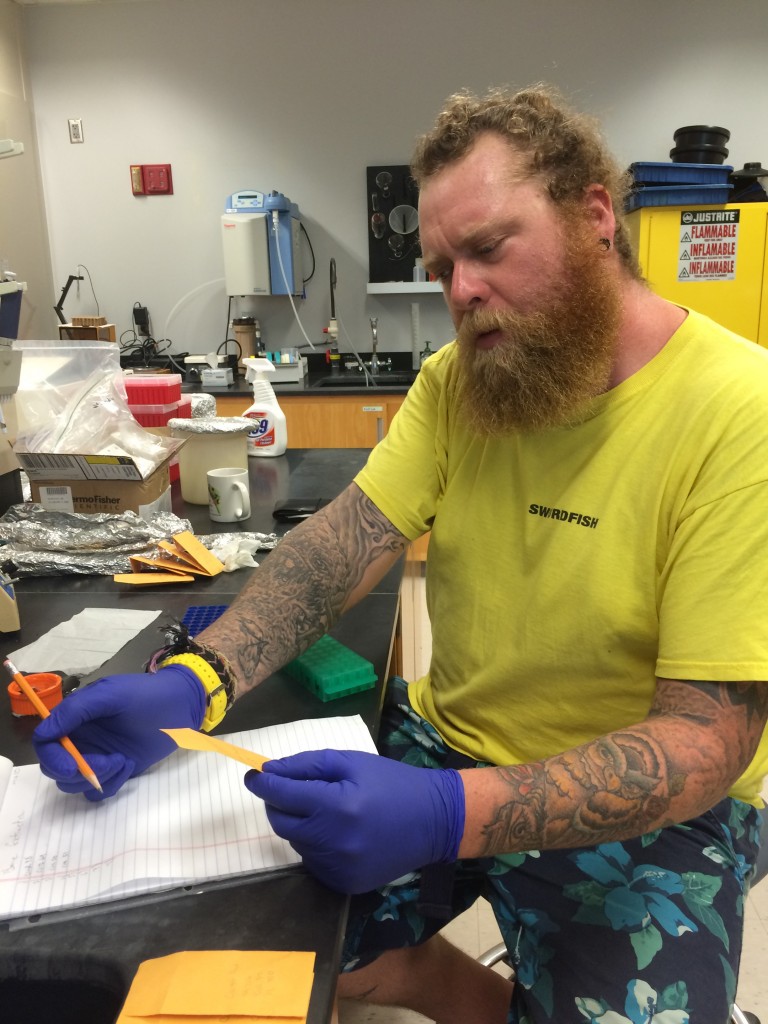
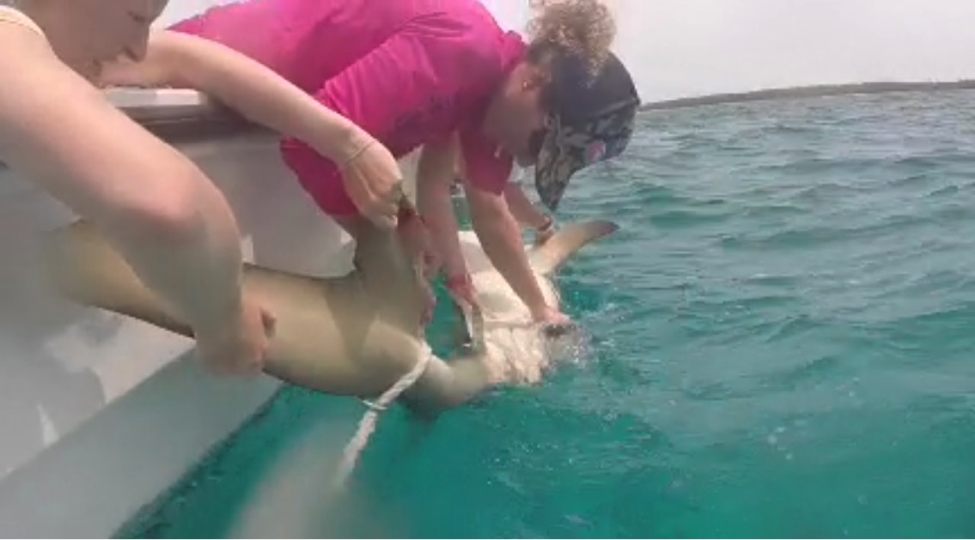
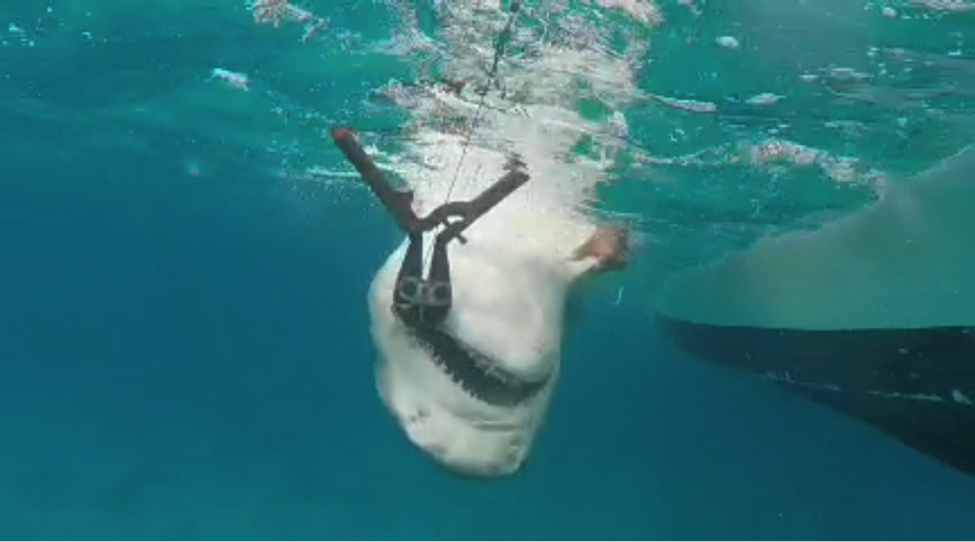
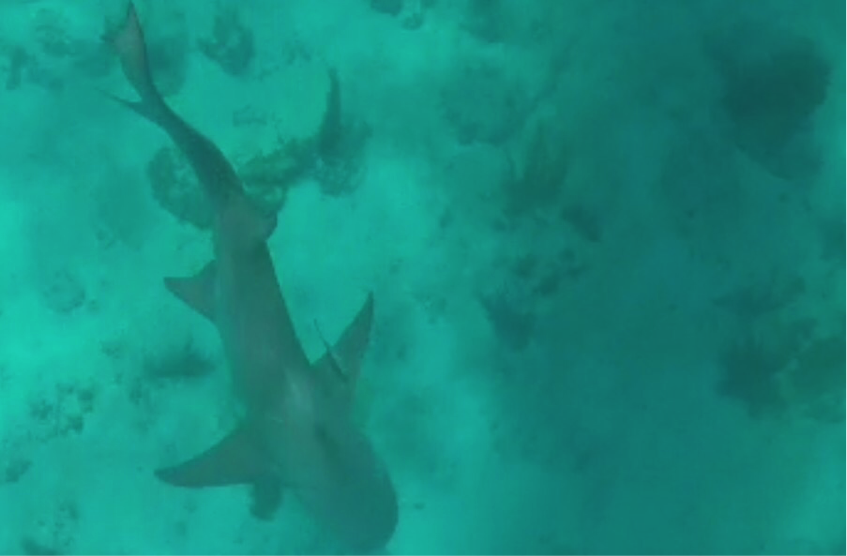
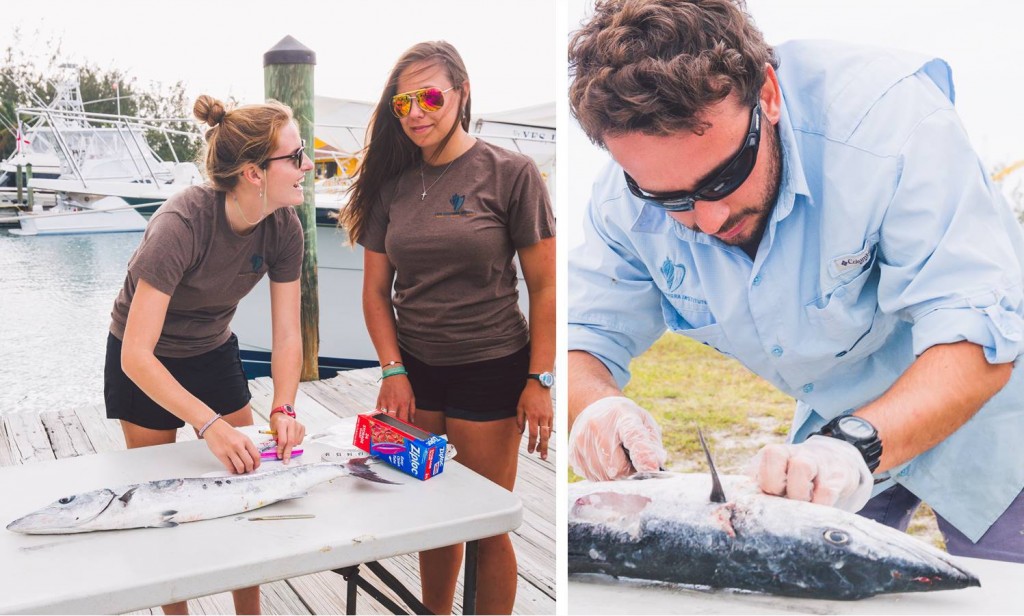
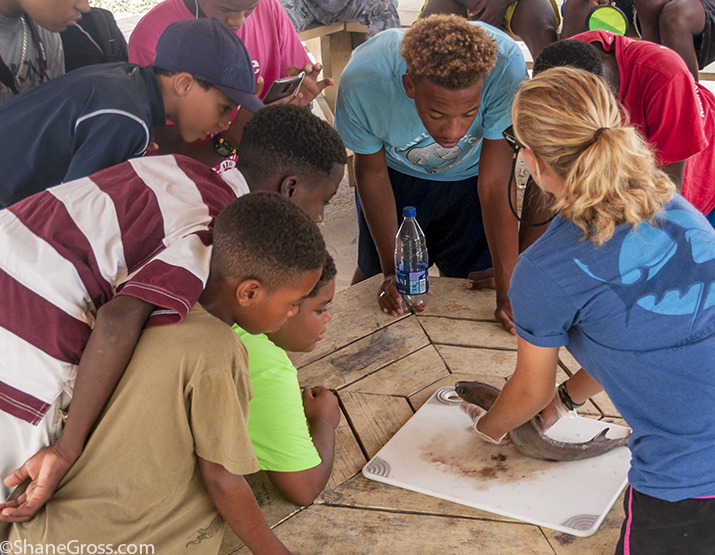
The following morning, the focus switched to the status of sharks in The Bahamas. Shane Gross, photojournalist specializing in underwater conservation photography, gave an insightful talk on sharks using many of his own photos and experiences. After this, Maggie Winchester, Research Technician at CEI, gave a presentation on the shark research currently going on at the institute, followed by a Cuban dogfish dissection.
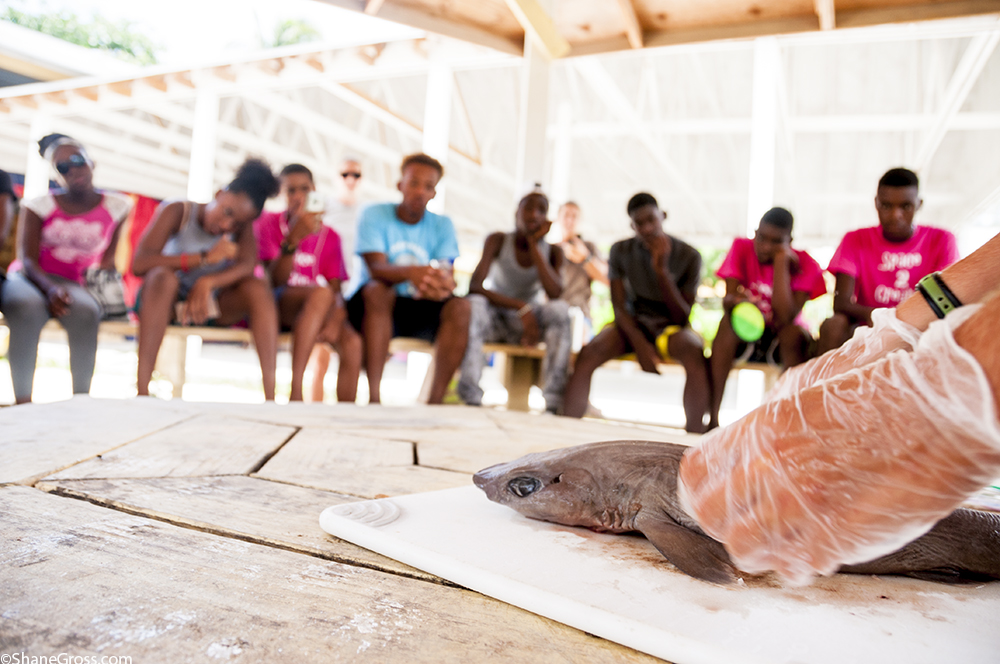

Sharks play a significant role in the marine ecosystems of The Bahamas, not only improving ecosystem health but aiding the tourism industry as well. Despite their importance, many species of shark remain vastly understudied. The Cuban dogfish is an abundant yet poorly understood species of deep water shark in The Bahamas, commonly found at around 600m depth. During the dissection, the campers learned about the internal and external adaptations that make this small species of shark able to survive and thrive deep in the water column. This provided a hands on opportunity to learn about shark biology, using a species commonly found around the Cape.
Between Shane and Maggie’s talks and the interaction with the Cuban dogfish, myths about sharks in the Bahamas were addressed and resolved, and many fears were removed.
In the future CEI will work in collaboration with Space 2 Create and Bahamas Plastic Movement to support research activities for Eleutheran Eco Schools Club ‘s.
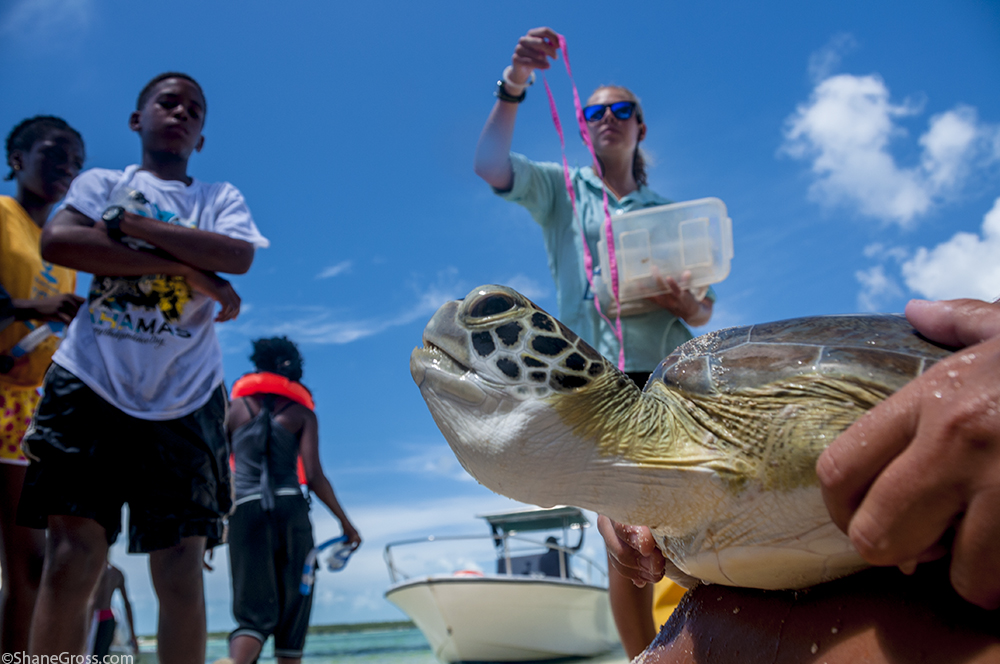

Photo credit: Shane Gross




 by
by